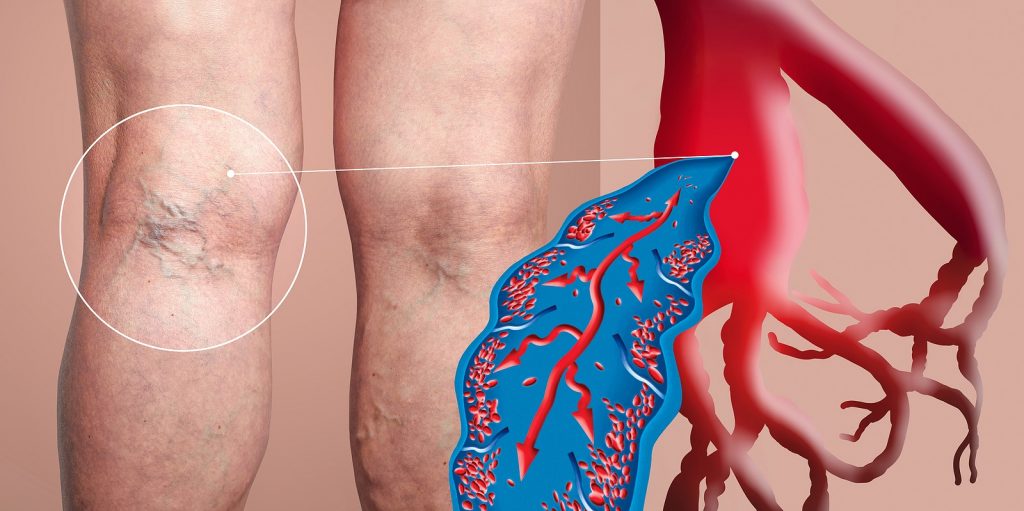
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that can lead to significant health complications if not appropriately diagnosed and treated. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) provides a standardized coding system that helps healthcare professionals accurately document DVT cases. By understanding the ICD-10 codes associated with deep vein thrombosis, both medical practitioners and patients can better navigate the complexities of this condition.
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, commonly in the legs, and can result in pain, swelling, and even life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes are crucial for effective management. With the increasing prevalence of DVT in today's society, particularly among those with sedentary lifestyles or certain medical conditions, knowledge about ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis is essential for timely intervention.
This article delves into the intricacies of ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis, exploring its definitions, coding specifics, and the importance of accurate diagnosis. We aim to equip readers with the necessary information to understand this condition better, whether they are healthcare professionals or individuals seeking to educate themselves about DVT.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs. It often presents with symptoms such as:
- Swelling in one leg
- Pain or tenderness
- Skin discoloration
- Warmth in the affected area
Understanding DVT is crucial for prevention and treatment, as untreated clots can dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
How is ICD-10 Used for Deep Vein Thrombosis?
The ICD-10 coding system is used by healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures. For deep vein thrombosis, specific codes help in documenting the condition accurately. The primary codes for DVT in ICD-10 include:
- I82.90: Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremities
- I82.91: Acute embolism and thrombosis of right deep vein of lower extremity
- I82.92: Acute embolism and thrombosis of left deep vein of lower extremity
Correct use of these codes is vital for patient management and insurance reimbursements.
What are the Risk Factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis, including:
- Prolonged immobility (e.g., long flights or bed rest)
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., cancer, heart disease)
- Hormonal therapy or pregnancy
Identifying and managing these risk factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of DVT.
How is Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and imaging tests. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Doppler ultrasound
- CT or MRI scans
- Blood tests (D-dimer test)
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent complications.
What Treatment Options are Available for DVT?
Treatment for deep vein thrombosis focuses on preventing clot growth and reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism. Common treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Thrombolytics (clot dissolvers)
- Compression stockings
Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual, depending on the severity of the condition and underlying health factors.
Can Deep Vein Thrombosis be Prevented?
While not all cases of DVT can be prevented, several strategies can reduce the risk, such as:
- Maintaining an active lifestyle
- Staying hydrated during long trips
- Wearing compression stockings when necessary
- Avoiding smoking and managing weight
Awareness and proactive measures can significantly decrease the incidence of DVT.
What is the Prognosis for Deep Vein Thrombosis?
The prognosis for individuals diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis varies based on several factors, including the location and extent of the clot, treatment efficacy, and the presence of comorbid conditions. With appropriate treatment, most individuals can recover fully and lead healthy lives.
Conclusion: Why Understanding ICD-10 Deep Vein Thrombosis is Important?
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients. Accurate diagnosis and coding can lead to improved treatment outcomes and better management of this serious condition. By being informed about DVT, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and seek timely intervention, ultimately leading to healthier lives.